Prostatic enlargement is a common condition men have with aging. More than 50% of men above 60 years of age have this condition.
Prostate enlargement has many consequences on the urinary tract affecting the quality of life. So, what’s prostatic enlargement? its causes, and what is the latest treatment for enlarged prostate?
What is prostatic enlargement?
Prostatic enlargement means that the prostate becomes bigger due to its overgrowth. Usually, it’s referred to as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
Normally, the prostate is located around the urethra (the tube through which urine passes from the bladder out). And it’s important for the viability of the sperms.
Enlargement is a physiological event that arises as a result of the regular proliferation of prostate glandular cells and vacuoles.
Being enlarged, the prostate compresses the urethra and affects the urine and semen outflow. So, prostatic enlargement can lead to urinary incontinence and fertility problems.
read here more about Urinary incontinence treatment dubai
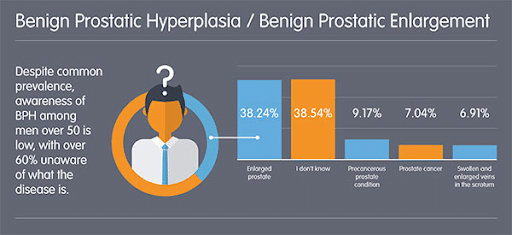
Prostate enlargement statistics:
The majority of the population suffers from these symptoms between the ages of 50-64 which is 50% and between the ages of 65-74 is 70%.
Learn more about prostate enlargement with Prof. Samir Al Sammerai: Here
What are the causes of prostatic enlargement?
Prostatic enlargement is considered a normal consequence of aging. About 80% of men in their nineties have an enlarged prostate.
However, the specific underlying causes for prostate enlargement or BPH are not yet identified. yet, it’s associated with various factors such as:
1- Hormonal changes
Testes produce sex hormones like testosterone. It’s been noticed that testosterone levels affect the prostate’s size.
In patients with removed testes, it’s been noticed that the rate of prostate overgrowth is decreased.
2- Family history
The incidence of developing prostate enlargement increases in people with a positive family history of the disease or testicular diseases.
3- Genetic mutations
Recent studies have shown that the increase in the body’s susceptibility and readiness to the genetic pathological mutations in these cells that lead first to benign enlargement and then cancer due to the high rate of environmental and food contamination.
Symptoms of enlarged prostate
Symptoms of enlarged prostate vary according to the degree of the enlargement. they include:
- Urinary incontinence: being unable to control urination.
- Being unable to fully empty your bladder.
- Having to strain during urination.
- Slow urine outflow.
- Increased voiding frequency in the night.
- Increased incidence of urinary tract infection.
The suffering from the enlargement is due to symptoms of narrowing of the urethra and the emptying of the bladder.
Complications of enlarged prostate
The Main causes of prostatic enlargement are advancing age, obesity, smoking, and recurrence of acute and chronic bacterial prostatitis.
This enlargement without treatment may lead over time to lower urinary symptoms with changes in bladder function, as well as may lead to recurrent acute and chronic urinary retention.
In case of this enlargement in the advanced stages, there is bladder dysfunction due to the narrowing of the urethra surrounded by this gland, leading later to pathological changes or deficiencies in the functions of the kidneys.
Diagnosis of prostatic enlargement
Diagnosis of prostatic enlargement/ BPH is done through:
- A physical examination includes a rectal examination to estimate the prostate’s size.
- History taking.
- Lab tests:
The physician may ask for lab tests to estimate the condition or to help him identify the underlying cause. they include:
Urine analysis.
Urine culture.
Prostate-specific antigen test to look for prostatic cancer.
Full blood picture.
Kidney function tests. - Cystoscopy to detect any problems in your bladder or urethra.
How to treat prostate enlargement?
The treatment prescribed depends on the degree of the enlargement and the severity of symptoms. Here’s how a normal treatment plan works:
1- Changing your style of living
This is the first step in treatment. It safely helps to control the symptoms of prostate enlargement. and it’s done as follows:
- Don’t hold it in. urinate when you feel the urge.
- Don’t drink a lot of water at a time, rather divide them along the day.
- Reduce water intake at night.
- Follow a balanced diet with little salt and spices.
- Restrict caffeine and soft drinks intake.
- Exercise your pelvic floor muscles by kegel exercise.
- Use daily pads.
- Don’t take decongestant drugs without a doctor’s permission.
2- Medications
your physician will prescribe you medication if changing your style of living isn’t enough to control your symptoms. these medications include:
- Alpha-blockers like tamsulosin help your prostate and bladder muscles to relax.
- Anticholinergic drugs also relax your prostate and bladder.
- Antiandrogenic drugs like finasteride that lower the level of your testosterone to decrease the size of the gland.
- Desmopressin helps you control urination at night.
- Antibiotics in case of inflammation or infection.
3- Catheters
Catheters are used when you can’t urinate. That can happen when the prostate enlargement is too advanced and it blocks the urine outlet.
It is done by inserting a tube inside your bladder to drain out the urine. The tube enters from the external meatus of the urethra or through a hole made above your pubic bone.
It’s a safe procedure and the tube can stay in for as long as needed.
4- Surgery
when none of the above works in controlling the symptoms, or when the symptoms aggravate, surgery may be indicated for treatment.
The surgical operations done to treat prostate enlargement include:
5- Outpatient surgeries
These are some minor procedures that don’t require staying long in the hospital after they are done. they include:
- Rezum: using thermal energy for reducing the enlargement.
- Transurethral microwave thermotherapy: using microwaves to reduce the enlargement.
- High-intensity focused ultrasound: a minimally invasive procedure where focused ultrasound is used to cut part of the prostate tissue.
- Urolift: holding back the enlarged parts of the prostate that pressure the urethra.
6- Inpatient surgeries
These types of surgeries are indicated when other ways fail or when your symptoms deteriorate causing kidney failure, persistent urinary incontinence, or recurrent infection. they include:
- Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP).
In this surgery, a device called a resectoscope is passed through the urethra to take the prostate off gradually. This procedure is the most performed surgery in treating prostate enlargement.
- Prostatectomy to remove the prostate or part of it.
What is the latest treatment for enlarged prostate?

As medical innovation never ceases, there have been new treatment methods for prostate enlargement that provide less invasive alternatives to surgery. So, what’s the latest treatment for enlarged prostate?
1- Prostate hydroablation (Aquablation)
It’s a modern procedure done with the help of robotic execution. it is done as follows:
- Using transrectal ultrasounds to map the anatomical features of the prostate before and during the procedure.
- Entering a handpiece of the aquabeam system that jets water streams at high velocity with accuracy.
- The water jet ablates the obstructing parts of the prostate without using any heat.
- The handpiece is removed and the bladder is washed out using a cystoscope.
- A ballooned catheter is inserted to stop any bleeding and to help the urethra remain open during healing.
So, this procedure provides accuracy and minimal postoperative complications.
2- Prostate artery embolism (PAE)
This procedure’s concept depends on decreasing the blood supply to the prostate thus decreasing the prostate abnormal growth. It’s done as follows:
- A catheter is inserted in the femoral artery in the upper thigh area or the radial artery in the wrist.
- The catheter is moved along the vessels under the guidance of x-ray imaging until it reaches the blood vessels supplying the prostate.
- Occluding chemicals are inserted into the blood vessels supplying the prostate thus obstructing them.
This procedure has shown good prognosis rates in the short time after its performance.
Prof. Al Samarrai Medical Center For Prostate Enlargement Treatment in Dubai
A man with these symptoms of BPH should contact us immediately:
- Inability to urinate.
- Painful urination.
- Fever of more than 38 degrees Celsius.
- Chills, or body aches.
- Pain in his lower back, just below the rib cage, is not related to an injury or physical effort.
- Blood or pus present in his urine or semen.
Trusting us will offer you the best:
- 30 years German experience.
- We provide the best treatment plan for each patient.
- A large number of successes in the treatment of intractable cases.
- Experience in dealing with the elderly and understanding their problems.
- Providing the highest quality medical care, whether in treatment, diagnosis or follow-up.
Still asking what’s the latest treatment for enlarged prostate? Call us, make an appointment and you will find out.